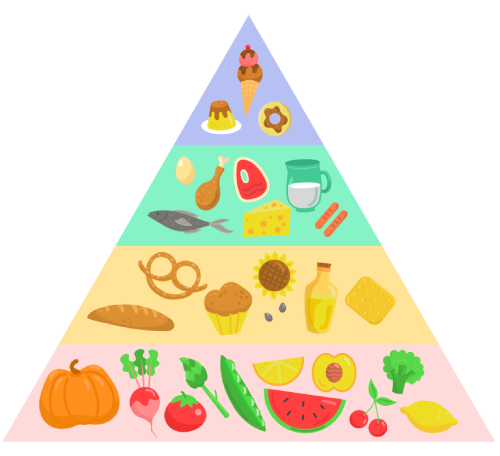
Avoid foods from the bottom of the pyramid due to their high calorie content and low nutritional value.
Understanding the factors contributing to obesity is key to addressing it effectively. It is a multifaceted issue influenced by an array of biological, behavioral, and environmental factors that all contribute to an individual’s risk of becoming obese.
Content
ToggleBiological Factors
Genetics can play a significant role in obesity, influencing how body fat is stored and distributed. Additionally, hormonal imbalances, such as those involving leptin and insulin, may affect appetite and metabolism. Medical conditions like hypothyroidism and polycystic ovary syndrome can also contribute to weight gain.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Factors
Diet and physical activity greatly impact body weight:
- High-Calorie Diets: Consumption of energy-dense foods high in fats and sugars leads to excessive calorie intake.
- Lack of Physical Activity: The prevalence of sedentary activities, such as screen time and desk jobs, reduces caloric expenditure.
- Psychological Influences: Stress, emotional eating, and sleep deprivation can adversely affect weight control and contribute to obesity.
Environmental and Societal Influences
The modern environment often promotes unhealthy lifestyle choices:
- Food Environment: Easy access to fast food and processed snacks makes unhealthy eating convenient and enticing.
- Urbanization: Infrastructures lacking pedestrian pathways and recreational areas discourage physical activity.
- Socioeconomic Status: Limited resources and education levels often restrict access to healthy foods and exercise facilities.
Desire: Strategies for Managing Obesity
Combatting obesity requires a comprehensive approach, addressing both the root causes and the symptomatic challenges of excess weight.
Long-term success hinges on sustainable lifestyle changes that encompass diet, exercise, and behavioral modifications.
Dietary Changes
Transforming your diet involves:
- Balanced Nutrition: Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to create satisfying, nutrient-rich meals.
- Portion Control: Understanding portion sizes and mindful consumption can prevent overeating and reduce calorie intake.
- Limiting Sugars and Fats: Reducing consumption of added sugars and saturated fats can significantly decrease caloric density.
Incorporating Physical Activity
Regular exercise is vital in weight management and overall health:
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Activities such as walking, jogging, or cycling increase caloric expenditure and improve cardiovascular fitness.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass boosts metabolism and aids in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Daily Movement: Simple lifestyle modifications, like taking stairs or walking during breaks, add to daily energy expenditure.
Behavioral and Psychological Support
Altering long-term habits is crucial:
- Goal Setting: Establish realistic, measurable objectives to guide your weight management journey.
- Professional Support: Engage with healthcare providers, nutritionists, or psychological coaches for personalized guidance and encouragement.
- Peer Support Groups: Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges offers reassurance and motivation.
Action: Taking Empowered Steps Toward Change
- Assess Your Lifestyle: Understand your current habits and identify areas for improvement.
- Create a Plan: Develop a structured plan incorporating dietary changes, exercise, and behavioral strategies tailored to your needs.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly track weight, activity, and dietary habits to measure success and make necessary adjustments.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest health information and research regarding obesity and weight management.
- Celebrate Achievements: Recognize and reward progress to maintain motivation and commitment to lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
The journey to overcoming obesity is a complex but achievable one, requiring dedication, education, and support.
By understanding the diverse factors contributing to obesity and employing a multifaceted approach to tackle them, individuals can achieve healthier body weights and improved well-being.
Remember that obesity is a disease like many others. Don’t hesitate to go to a specialist to see your specific case.
The doctor needs to know the cause of your obesity: family history, eating habits, high stress, hormones, alcohol intake, lack of exercise in your routine.
A nutritionist professional can help you change your eating habits so that you can enjoy making changes and substitutions to your menu.
But all this requires determination and resilience, as with any change of habit. And it doesn’t just happen. It takes courage and going step by step to regain your more balanced health.
Another tip: find a hobby that gives you pleasure, meditate and don’t close yourself off from the world. Everyone has the right to be happy.